
Boys are at least four times as likely as girls to develop the disorder (4:1); indeed some studies have found that boys with ADHD outnumber girls with the condition by nine to one (9:1), possibly because boys are genetically more prone to disorders of the nervous system. In children between ages 5 and 15 years it was found that 3.62% of boys and 0.85% of girls have ADHD (Ford et al., 2003). In adults 3.4 % (1.2 to 7.3 %) are presented with ADHD, in individuals aged 18 – 44 years in low-income countries (1.9%) and in high-income countries (4.2%). (Fayyad et al., 2007; Barkley R et al., 2006). 0.6 –1.2% of adults retains the childhood diagnosis ADHD by the age of 25 years.
The causes of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder still remain unknown. It is transmitted in families and most likely is due to the influence of multimodal factors, e.g., the result of a complex set of factors including genetic inheritance, environmental factors, function in several brain regions and level of neurotransmitter activity. It is believed that mutations in several genes that are normally very active in the prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia, tends to play role in the genesis of ADHD. 
The essential features of ADHD continue to include the triad of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. There are three subtypes: predominantly hyperactive –impulsive type, the predominantly inattentive type (PI), and the combined type. The DSM IV criteria indicate that symptoms must be present for at least 6 months, with onset before age 7. Attention span and sitting tolerance increases with the age of child. Inattention appears to be more evident in girls. The symptoms of the disorder can cause problems in learning; socialization and behavior for those individuals afflicted with it and put them at high risk for serious psychopathology in adulthood. There is growing literature on the ADHD- PI subtype with even later age of onset. These children have lower comorbidity with disruptive disorders, and higher levels of substance abuse, anxiety and mood disorders.
There are developmental differences in the presentation of symptoms. Given below are some of them:
Preschoolers:
- Gross motor hyperactivity- running, climbing
- Difficulty remaining quiet
- Non-compliant
- 3-5 years onset – 50% of them continue to have ADHD
School age:
- Difficulty focusing
- Losing things
- Forgetfulness
- Poor Organizing
- Adolescents
- Incomplete assignments and projects
- Academic under-performance
- Conflicts with peers, teachers and parents
- Poor planning, organizing skills
Management involves two phases: Assessment and Treatment
Assessments are usually multimodal: Interview: Parent and Child, Observation, School workbook, Individual testing: cognitive functions, Rating Scale- Parent, Teacher, Self-report (e.g., Conners rating scale; Vanderbilt scale)
Treatment: Psychological and pharmacological Intervention of child ADHD

Conclusion: Despite considerable progress over the past three decades, much is to be learned regarding the neurophysiological basis and genetics of ADHD. Psychological Assessment can serve to essentially validate the diagnosis of ADHD in children and Adults. There have been considerable advances in psychosocial, pharmacological and multimodal treatment of ADHD.
 Subsequently, this often results in chronic depression, poor scholastic performance, psycho-social problems, substance abuse and even suicide. It’s equally prevalent in both sexes during pre-puberty stage whereas more in females with a ratio of 2:1 post-puberty. Mean duration of an episode of depression is 7 to 9 months. 70 to 80 % recover at the end of one year. Increased chance of recurrence is seen in children with early onset and those with the history of previous episodes, co-morbid psychotic symptoms, poor drug compliance, negative life events and positive family history in parents. 20 to 30 % of depressive children develop manic episodes (Bipolar Disorder) on follow up.
Subsequently, this often results in chronic depression, poor scholastic performance, psycho-social problems, substance abuse and even suicide. It’s equally prevalent in both sexes during pre-puberty stage whereas more in females with a ratio of 2:1 post-puberty. Mean duration of an episode of depression is 7 to 9 months. 70 to 80 % recover at the end of one year. Increased chance of recurrence is seen in children with early onset and those with the history of previous episodes, co-morbid psychotic symptoms, poor drug compliance, negative life events and positive family history in parents. 20 to 30 % of depressive children develop manic episodes (Bipolar Disorder) on follow up. Few predisposing factors/ vulnerability factors are: Genetic; biological factors (neurotransmitters -monoamine metabolism and endocrine abnormalities); and temperament (e.g. quiet children with regular habits and slow to adapt to new experiences). Chronic life adversities are also likely to contribute to develop depression – broken homes, parental alcoholism, abuse, rejection etc. Undesirable life events in previous 12 months are important e.g., an event at home, or school and experience of loss.
Few predisposing factors/ vulnerability factors are: Genetic; biological factors (neurotransmitters -monoamine metabolism and endocrine abnormalities); and temperament (e.g. quiet children with regular habits and slow to adapt to new experiences). Chronic life adversities are also likely to contribute to develop depression – broken homes, parental alcoholism, abuse, rejection etc. Undesirable life events in previous 12 months are important e.g., an event at home, or school and experience of loss. disability by obtaining the history from all available sources; to explore into the stressors in the school/home; to consider differential diagnosis – Physical conditions like hypothyroidism; psychosis; normal reactive feelings of sadness and unhappiness; look for co morbid condition.
disability by obtaining the history from all available sources; to explore into the stressors in the school/home; to consider differential diagnosis – Physical conditions like hypothyroidism; psychosis; normal reactive feelings of sadness and unhappiness; look for co morbid condition.

 They can’t control their negative thoughts and don’t believe people who tell them that they look fine. Their thoughts may cause severe emotional distress and interfere with their daily functioning. They may miss work or school, avoid social situations and isolate themselves, even from family and friends, because they fear others will notice their flaws.
They can’t control their negative thoughts and don’t believe people who tell them that they look fine. Their thoughts may cause severe emotional distress and interfere with their daily functioning. They may miss work or school, avoid social situations and isolate themselves, even from family and friends, because they fear others will notice their flaws.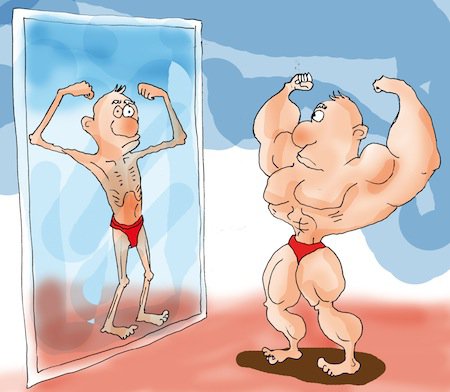




 The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) recognises that the existence of barriers constitutes a central component of disability.
The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) recognises that the existence of barriers constitutes a central component of disability.
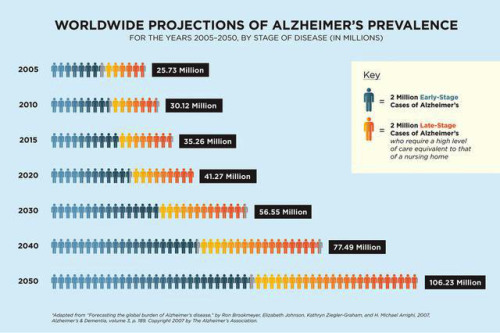
 Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Symptoms usually develop slowly and get worse over time, becoming severe enough to interfere with daily tasks.
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Symptoms usually develop slowly and get worse over time, becoming severe enough to interfere with daily tasks. People with memory loss or other possible signs of Alzheimer’s may find it hard to recognize they have a problem. Signs of dementia may be more obvious to family members or friends. Anyone experiencing dementia-like symptoms should see a doctor as soon as possible. At International Modern Hospital, we offer specialised care for such patients under the guidance of our psychiatrist,
People with memory loss or other possible signs of Alzheimer’s may find it hard to recognize they have a problem. Signs of dementia may be more obvious to family members or friends. Anyone experiencing dementia-like symptoms should see a doctor as soon as possible. At International Modern Hospital, we offer specialised care for such patients under the guidance of our psychiatrist, 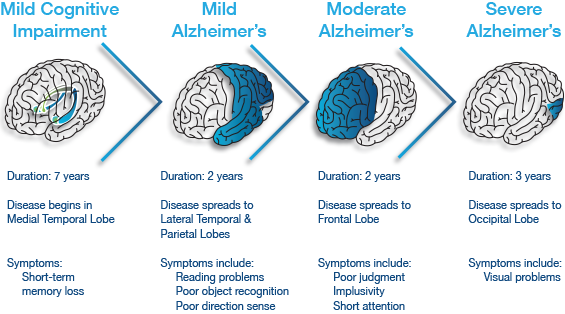
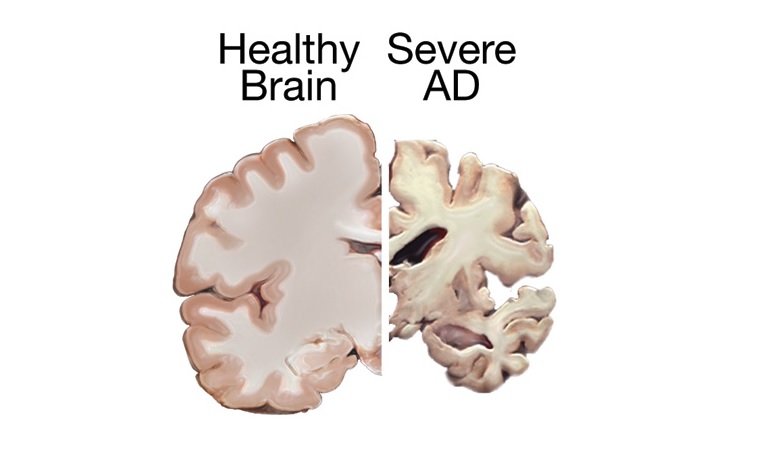 Plaques are deposits of a protein fragment called beta-amyloid (BAY-tuh AM-uh-loyd) that build up in the spaces between nerve cells.
Plaques are deposits of a protein fragment called beta-amyloid (BAY-tuh AM-uh-loyd) that build up in the spaces between nerve cells.
 The World Health Organization estimates that over 800,000 people die by suicide each year – that’s one person every 40 seconds. Up to 25 times as many again make a suicide attempt. There are many, many more people who have been bereaved by suicide or have been close to someone who has tried to take his or her own life. ‘Connect, communicate, care’ is the theme of the 2016 World Suicide Prevention Day. These three words are at the heart of suicide prevention.
The World Health Organization estimates that over 800,000 people die by suicide each year – that’s one person every 40 seconds. Up to 25 times as many again make a suicide attempt. There are many, many more people who have been bereaved by suicide or have been close to someone who has tried to take his or her own life. ‘Connect, communicate, care’ is the theme of the 2016 World Suicide Prevention Day. These three words are at the heart of suicide prevention. Social connectedness reduces the risk of suicide, so being there for someone who has become disconnected can be a life-saving act. Connecting them with formal and informal supports may also help to prevent suicide. Individuals, organisations and communities all have a responsibility here.
Social connectedness reduces the risk of suicide, so being there for someone who has become disconnected can be a life-saving act. Connecting them with formal and informal supports may also help to prevent suicide. Individuals, organisations and communities all have a responsibility here. Open communication is vital if we are to combat suicide. We need to discuss suicide as we would any other public health issue if we are to dispel myths about it and reduce the stigma surrounding it. Equipping people to communicate effectively with those who might be vulnerable to suicide is an important part of any suicide prevention strategy. Showing compassion and empathy, and listening in a non-judgemental way is very important.
Open communication is vital if we are to combat suicide. We need to discuss suicide as we would any other public health issue if we are to dispel myths about it and reduce the stigma surrounding it. Equipping people to communicate effectively with those who might be vulnerable to suicide is an important part of any suicide prevention strategy. Showing compassion and empathy, and listening in a non-judgemental way is very important. All the connecting and communicating in the world will have no effect without care. We need to ensure that we are caring ourselves. We need to look out for others who may be struggling, and let them tell their story in their own way and at their own pace.
All the connecting and communicating in the world will have no effect without care. We need to ensure that we are caring ourselves. We need to look out for others who may be struggling, and let them tell their story in their own way and at their own pace.

 Children are not immune to forces that have driven many adults toward healthy lifestyles and spa and wellness therapies. They too are living in an electronic-gadget-obsessed world, crouching over devices, as they’re fed information and images at incredible speed. Children spend more time than ever hunched over glowing screens.
Children are not immune to forces that have driven many adults toward healthy lifestyles and spa and wellness therapies. They too are living in an electronic-gadget-obsessed world, crouching over devices, as they’re fed information and images at incredible speed. Children spend more time than ever hunched over glowing screens.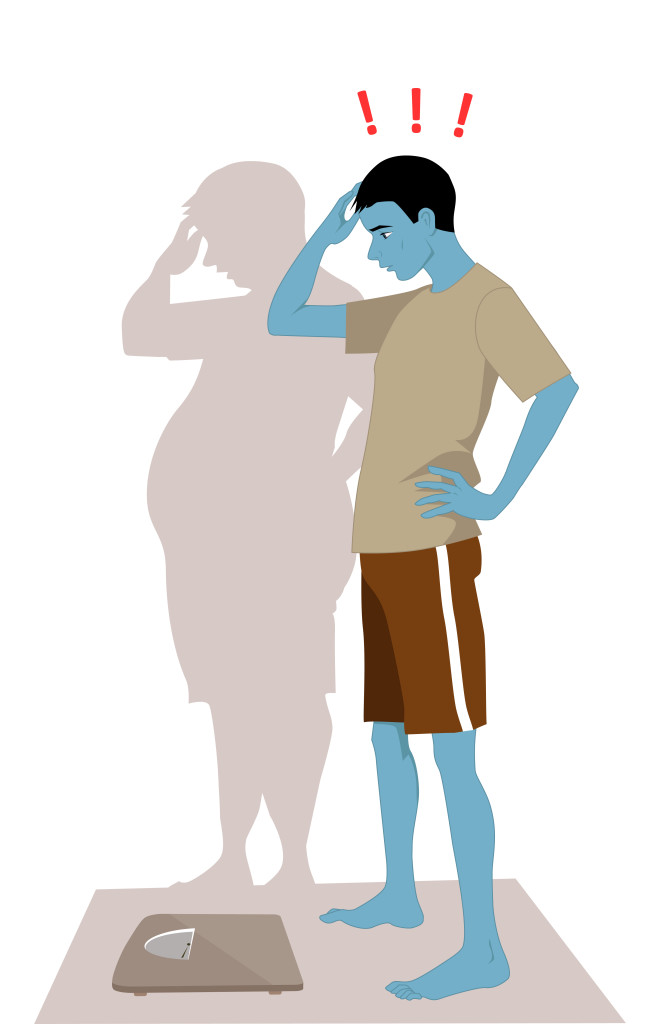 Anorexia Nervosa is a psychological and possibly life-threatening eating disorder defined by an extremely low body weight relative to stature (this is called BMI [Body Mass Index] and is a function of an individual’s height and weight), extreme and needless weight loss, illogical fear of weight gain, and distorted perception of self-image and body.
Anorexia Nervosa is a psychological and possibly life-threatening eating disorder defined by an extremely low body weight relative to stature (this is called BMI [Body Mass Index] and is a function of an individual’s height and weight), extreme and needless weight loss, illogical fear of weight gain, and distorted perception of self-image and body.