Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt
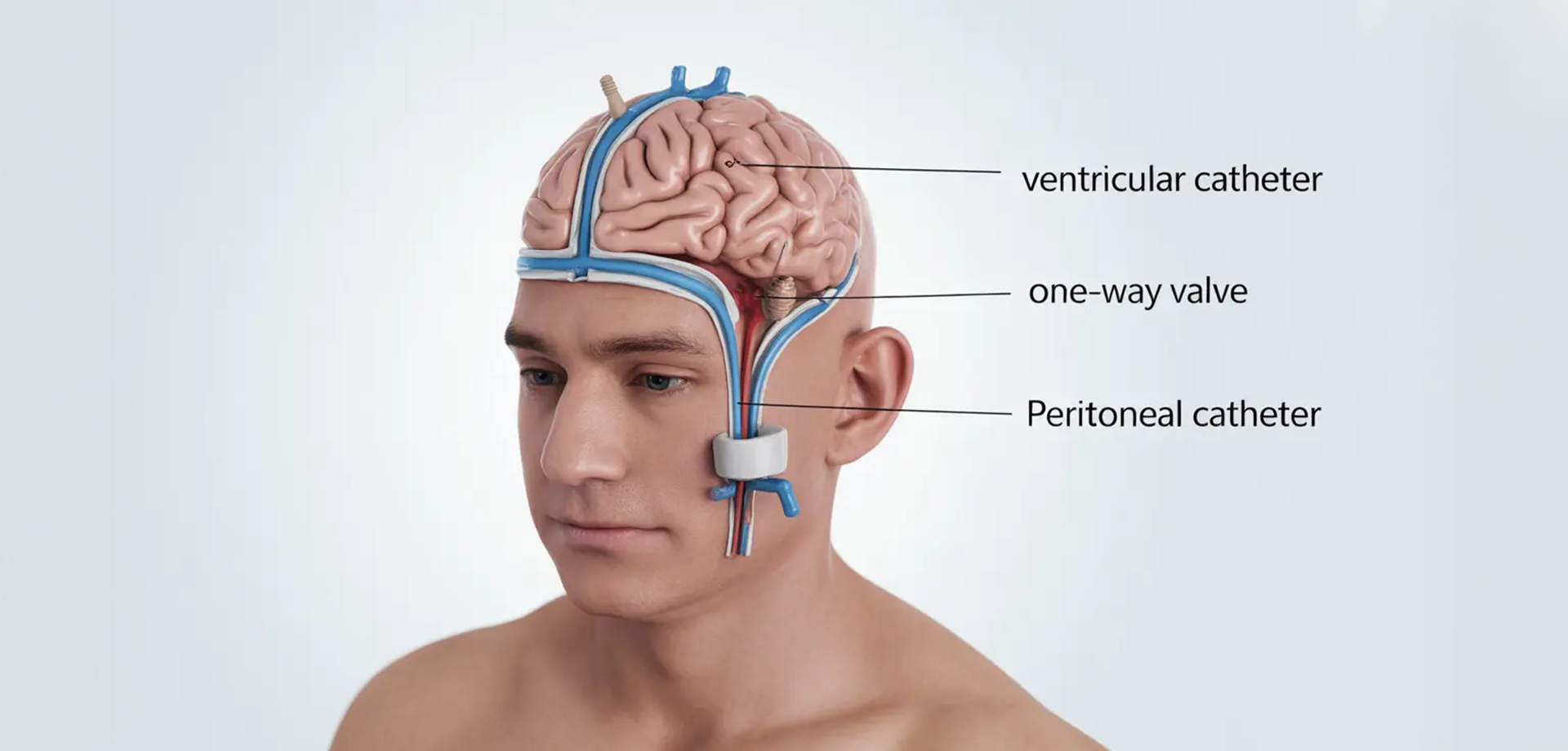
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt surgery is a specialized neurosurgical procedure performed to treat hydrocephalus, a condition characterized by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain’s ventricular system. In the UAE’s advanced neuroscience centers, VP shunt placement remains a cornerstone intervention for both pediatric and adult hydrocephalus, addressing pressure buildup that may otherwise lead to neurological deterioration. Hydrocephalus can result from congenital abnormalities, brain tumors, hemorrhage, infection, trauma, or impaired cerebrospinal fluid absorption, and timely surgical intervention is critical to prevent progressive brain injury.
The VP shunt system functions by diverting excess fluid from the brain’s ventricles to the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen, where it can be absorbed naturally. This diversion reduces intracranial pressure and alleviates associated symptoms such as headaches, nausea, gait disturbance, cognitive changes, or developmental delay in children. In Dubai’s tertiary hospitals, pre-operative evaluation typically includes MRI or CT imaging to assess ventricular enlargement and determine optimal catheter placement pathways.
The surgical procedure involves inserting a catheter into the ventricular system through a carefully planned cranial entry point. The catheter is then connected to a valve mechanism that regulates fluid flow before being tunneled beneath the skin to the abdominal cavity. Precision in placement is essential to ensure effective drainage while minimizing complications. Advanced operating suites across UAE neuroscience programs incorporate neuro-navigation tools to enhance accuracy and reduce procedural risk.
Post-operative monitoring is conducted within specialized neurocritical care units, where neurological status and shunt function are closely observed. Imaging may be performed to confirm correct positioning and adequate ventricular decompression. Long-term follow-up is essential, as shunt systems require monitoring for potential blockage, malfunction, or infection. In the UAE, structured follow-up protocols emphasize early recognition of shunt-related complications and coordinated multidisciplinary care.
VP shunt surgery remains one of the most effective interventions for hydrocephalus management when conservative measures are insufficient. The procedure has evolved significantly with improved valve technologies and imaging guidance, enhancing safety and functional outcomes. Dubai’s neuroscience centers are increasingly recognized for their capability in managing complex hydrocephalus cases, including congenital and tumor-related conditions.
Hydrocephalus can affect patients across all age groups, from newborns to elderly individuals with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Early diagnosis and timely shunt placement are critical to preserving neurological function and quality of life. Within the UAE’s advanced healthcare ecosystem, integrated neurosurgical and rehabilitation pathways ensure continuity of care following shunt surgery. The availability of modern infrastructure and multidisciplinary expertise reinforces the region’s growing reputation in complex brain and cerebrospinal fluid disorder management.
The VP shunt system functions by diverting excess fluid from the brain’s ventricles to the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen, where it can be absorbed naturally. This diversion reduces intracranial pressure and alleviates associated symptoms such as headaches, nausea, gait disturbance, cognitive changes, or developmental delay in children. In Dubai’s tertiary hospitals, pre-operative evaluation typically includes MRI or CT imaging to assess ventricular enlargement and determine optimal catheter placement pathways.
The surgical procedure involves inserting a catheter into the ventricular system through a carefully planned cranial entry point. The catheter is then connected to a valve mechanism that regulates fluid flow before being tunneled beneath the skin to the abdominal cavity. Precision in placement is essential to ensure effective drainage while minimizing complications. Advanced operating suites across UAE neuroscience programs incorporate neuro-navigation tools to enhance accuracy and reduce procedural risk.
Post-operative monitoring is conducted within specialized neurocritical care units, where neurological status and shunt function are closely observed. Imaging may be performed to confirm correct positioning and adequate ventricular decompression. Long-term follow-up is essential, as shunt systems require monitoring for potential blockage, malfunction, or infection. In the UAE, structured follow-up protocols emphasize early recognition of shunt-related complications and coordinated multidisciplinary care.
VP shunt surgery remains one of the most effective interventions for hydrocephalus management when conservative measures are insufficient. The procedure has evolved significantly with improved valve technologies and imaging guidance, enhancing safety and functional outcomes. Dubai’s neuroscience centers are increasingly recognized for their capability in managing complex hydrocephalus cases, including congenital and tumor-related conditions.
Hydrocephalus can affect patients across all age groups, from newborns to elderly individuals with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Early diagnosis and timely shunt placement are critical to preserving neurological function and quality of life. Within the UAE’s advanced healthcare ecosystem, integrated neurosurgical and rehabilitation pathways ensure continuity of care following shunt surgery. The availability of modern infrastructure and multidisciplinary expertise reinforces the region’s growing reputation in complex brain and cerebrospinal fluid disorder management.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







