GLP-1 / GIP Therapies
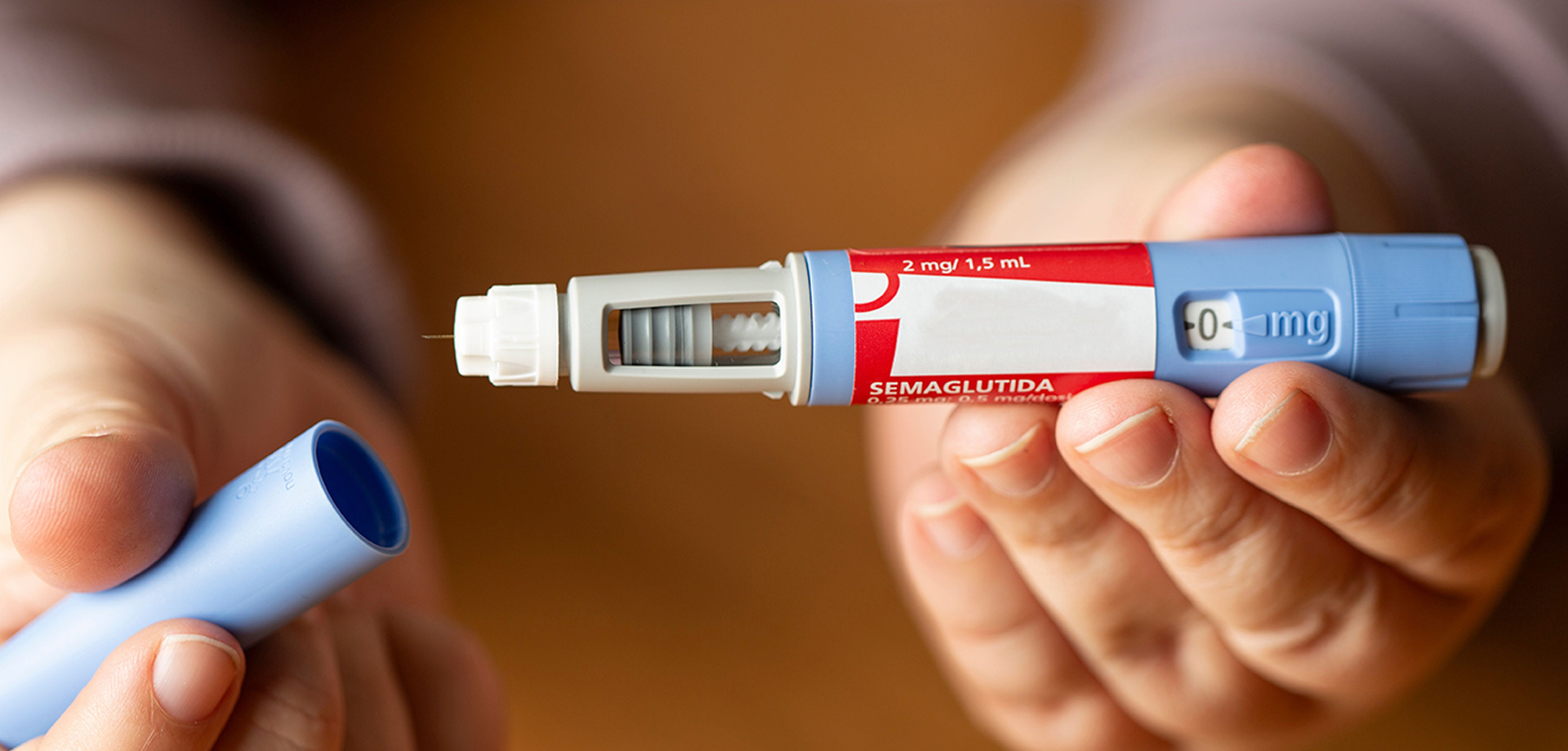
GLP-1 and dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist therapies represent a major advancement in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes and obesity-related metabolic disease. These therapies are based on incretin hormones that enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppress inappropriate glucagon release, slow gastric emptying, and promote satiety. By addressing multiple metabolic pathways simultaneously, GLP-1 and GIP-based therapies offer effective glycemic control with additional benefits on weight, cardiovascular risk, and metabolic health.
In individuals with Type 2 diabetes, impaired incretin response contributes to postprandial hyperglycemia and progressive beta-cell dysfunction. GLP-1 receptor agonists restore this pathway by enhancing insulin secretion only when blood glucose levels are elevated, significantly reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. Dual GLP-1/GIP therapies further amplify metabolic benefits by improving insulin sensitivity and energy balance through complementary hormonal action.
These therapies are particularly indicated for patients with inadequate glycemic control on oral medications, those with obesity or metabolic syndrome, and individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk. They are also valuable for patients who wish to delay or avoid insulin initiation while achieving meaningful glucose and weight reduction. Selection is individualized based on clinical profile, tolerability, and treatment goals.
Initiation of GLP-1/GIP therapy requires structured patient education. Patients are counseled on injection techniques, dose escalation schedules, expected appetite changes, and gastrointestinal side effects. Gradual dose titration minimizes nausea and improves long-term adherence. Ongoing monitoring ensures therapeutic effectiveness while identifying intolerance or contraindications early.
Beyond glucose control, these therapies offer significant cardiometabolic advantages. Clinical evidence demonstrates improvements in body weight, blood pressure, lipid profile, and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk populations. These benefits position GLP-1/GIP therapies as integral components of comprehensive metabolic care rather than glucose-lowering agents alone.
Long-term management includes regular assessment of glycemic response, weight trajectory, gastrointestinal tolerance, and patient satisfaction. When used appropriately within an endocrine-led treatment pathway, GLP-1 and GIP therapies improve metabolic control, reduce complication risk, and support sustainable lifestyle modification. Their integration reflects a shift toward holistic, outcomes-driven diabetes management.
In individuals with Type 2 diabetes, impaired incretin response contributes to postprandial hyperglycemia and progressive beta-cell dysfunction. GLP-1 receptor agonists restore this pathway by enhancing insulin secretion only when blood glucose levels are elevated, significantly reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. Dual GLP-1/GIP therapies further amplify metabolic benefits by improving insulin sensitivity and energy balance through complementary hormonal action.
These therapies are particularly indicated for patients with inadequate glycemic control on oral medications, those with obesity or metabolic syndrome, and individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk. They are also valuable for patients who wish to delay or avoid insulin initiation while achieving meaningful glucose and weight reduction. Selection is individualized based on clinical profile, tolerability, and treatment goals.
Initiation of GLP-1/GIP therapy requires structured patient education. Patients are counseled on injection techniques, dose escalation schedules, expected appetite changes, and gastrointestinal side effects. Gradual dose titration minimizes nausea and improves long-term adherence. Ongoing monitoring ensures therapeutic effectiveness while identifying intolerance or contraindications early.
Beyond glucose control, these therapies offer significant cardiometabolic advantages. Clinical evidence demonstrates improvements in body weight, blood pressure, lipid profile, and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk populations. These benefits position GLP-1/GIP therapies as integral components of comprehensive metabolic care rather than glucose-lowering agents alone.
Long-term management includes regular assessment of glycemic response, weight trajectory, gastrointestinal tolerance, and patient satisfaction. When used appropriately within an endocrine-led treatment pathway, GLP-1 and GIP therapies improve metabolic control, reduce complication risk, and support sustainable lifestyle modification. Their integration reflects a shift toward holistic, outcomes-driven diabetes management.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7



 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000







