What does (s) he understand?
- His or her complexity of understanding keeps extending. He / She now understands simple WHO? WHAT? And WHERE? Questions and hears you when you call from another room.
- This is the crucial age where hearing difficulties may become evident. If you are in a doubt of his/her hearing, it’s wise to consult an audiologist.
 What does (s) he speak?
What does (s) he speak?
- (S)he talks about many things to you, what happened in preschools, what type of play they did, how is teacher to him/her, what are his/her friends, what funny, and new (s)he experiences, and also his imaginations.
- His/her sentences are becoming longer and longer as (s) he combines four, five or more words. His /her speech is usually clear and fluent and easily understood by the strangers most of the time.
- They become very loud and unstoppable.
How can I help my child?
- Mix categories e.g. mix animals with picture of baby, cookies, ice cream. And make the child to sort them out and show what doesn’t belong to the category. Tell him/her that he is correct baby doesn’t belong to cat, dog, category because baby is not an animal.
- Draw, glue a car without wheels, favorite cartoon with a mistake, glue a dog in driving seat and talk about how silly the pictures and encourage him/her to talk about what is missing, and what is correct.
- Act out typical scenarios with the child like going to doctor with the pet, teacher and student, acting like the mother at home, cooking food, making baby dress up, superman. Allow her/him to guide you in acting. Be the student and let your child teach a lesson. Ask the child questions; make him repeat if you have not understood completely.
- Expand the child’s vocabulary by acting, storytelling, singing, filling the blanks. Talk about new games, new ideas you and your child can do and have fun.

- Find out a simple and interesting story book read line by line, ask simple WH questions (what, Where, Who, Why).Talk about favorite part in the story, in the cartoon. This is the best time to talk about favorite things with the child talk about his/her favorite game, food, rhymes and tell him/her also your choices.
- Bring your family album to the bed. Talk about the photo and ask the child can you remember this photo. Help him to explain what happened.
- Do silly mistakes in game, apologize for your mistakes, and ask his/her help to play correctly.

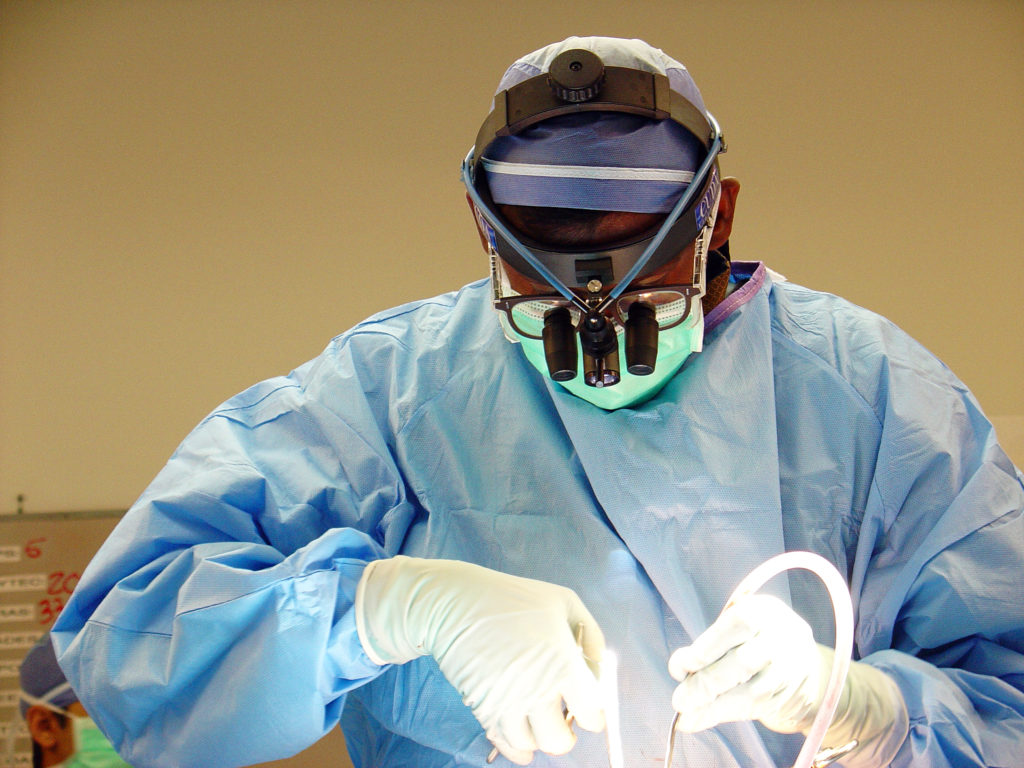
 It is important for these people to see a Surgeon at the earliest to enable an accurate diagnosis and initiate early treatment to prevent further complications. Over the counter medications and creams are of limited use as almost all of these conditions present with more or less the same complaints, however the treatment is completely different for each one of them.
It is important for these people to see a Surgeon at the earliest to enable an accurate diagnosis and initiate early treatment to prevent further complications. Over the counter medications and creams are of limited use as almost all of these conditions present with more or less the same complaints, however the treatment is completely different for each one of them.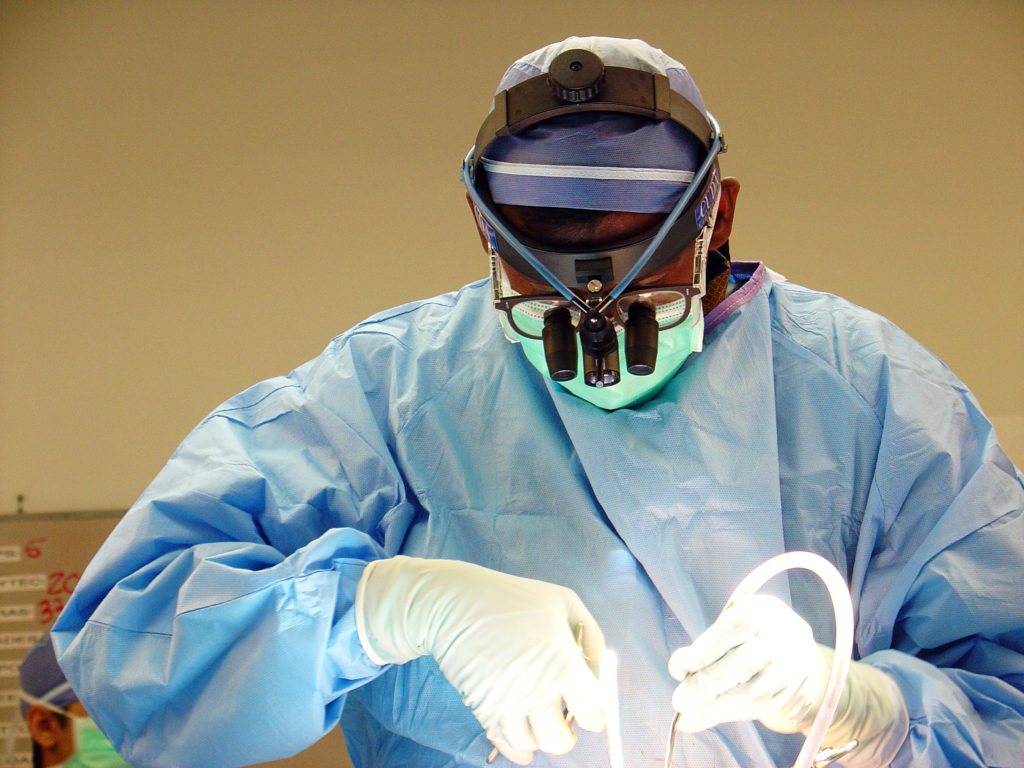 These however, need to be performed by experienced Surgeons who have undergone extensive training in this specialty and have the know how and technical expertise.
These however, need to be performed by experienced Surgeons who have undergone extensive training in this specialty and have the know how and technical expertise.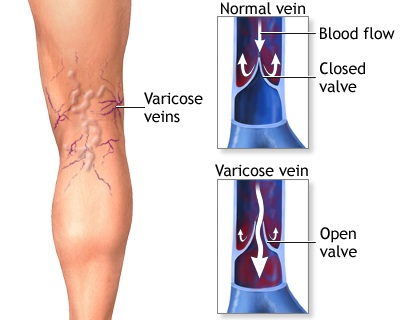
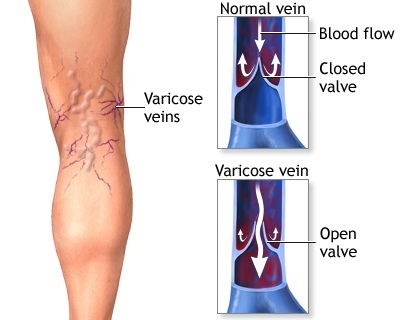 Varicose veins are swollen, twisted, and enlarged veins that you can see under the skin. They are often red or blue in color. They usually appear in the legs, but can occur in other parts of the body.
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted, and enlarged veins that you can see under the skin. They are often red or blue in color. They usually appear in the legs, but can occur in other parts of the body.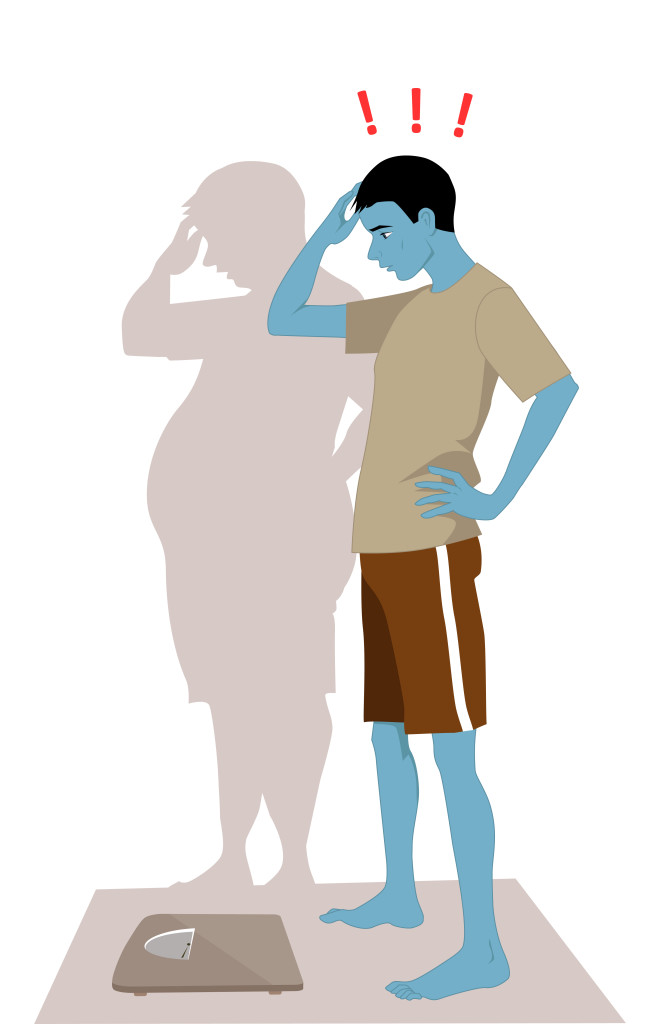 Anorexia Nervosa is a psychological and possibly life-threatening eating disorder defined by an extremely low body weight relative to stature (this is called BMI [Body Mass Index] and is a function of an individual’s height and weight), extreme and needless weight loss, illogical fear of weight gain, and distorted perception of self-image and body.
Anorexia Nervosa is a psychological and possibly life-threatening eating disorder defined by an extremely low body weight relative to stature (this is called BMI [Body Mass Index] and is a function of an individual’s height and weight), extreme and needless weight loss, illogical fear of weight gain, and distorted perception of self-image and body.