15 Mar 2024
Dr. Cumhur Kaan Yaltirik
Specialist Neurosurgeon
Visit Profile
Book Appointment
Introduction
This case study focuses on the effective management and treatment of a 57-year-old male patient diagnosed with a right frontoparietal parasagittal meningioma at the Department of Neurosurgery, International Modern Hospital. It showcases the hospital’s commitment to excellence in patient care and the utilization of advanced neurosurgical techniques.
Patient Background
The patient, with no significant past medical history, presented with symptoms of sudden onset weakness and numbness in the left arm and leg. These symptoms, developing over approximately a month, led to an acute exacerbation that necessitated emergency care.
Diagnosis | Right Frontoparietal Meningioma
Upon evaluation at the International Modern Hospital, a comprehensive neurological assessment was conducted. A Brain MRI revealed a right frontoparietal meningioma, leading to the patient’s admission to the neurosurgery ward for treatment.
Treatment
The treatment plan included a right frontoparietal parasagittal craniotomy, microsurgical removal of the tumour, and duraplasty with a galeal graft. Preoperative preparations involved antiedema and antiepileptic medications, alongside evaluations by the neurosurgery and anesthesiology teams, to ensure the patient was fit for surgery.
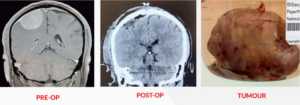
Clinical Progress and Outcome
Following surgery, the patient was closely monitored in the ICU, with a control CT scan showing no complications. Remarkably, the patient began mobilizing after being transferred to the ward. Neurological examinations post-surgery showed a complete return to normal function, with the surgical wound healing without issue. The patient did not develop any additional problems during follow-up and was discharged with comprehensive post-discharge care recommendations.
Histopathology Findings
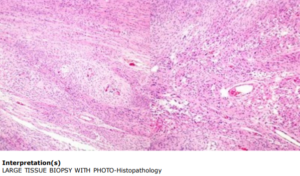
Discussion
Meningiomas are tumours that arise from the meninges, the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Although most meningiomas are benign (non-cancerous) and grow slowly, their location and size can lead to significant health issues, depending on their impact on the surrounding brain tissue and nerves.
Meningiomas can occur at any age but are most commonly diagnosed in adults, particularly in individuals over the age of 60. They are more prevalent in women than in men. The cause of meningiomas is not fully understood, but factors such as radiation exposure and genetic disorders have been linked to an increased risk of developing these tumours.
The symptoms of meningiomas vary widely and depend on the tumour’s size and location. Some individuals with small meningiomas may not experience any symptoms, and these tumours are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for unrelated conditions. However, larger tumours can cause symptoms such as:
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Vision problems
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears
- Memory or concentration issues
- Weakness in the arms or legs
- Speech difficulties
Diagnosing meningiomas typically involves a combination of neurological examination and imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. These tests help determine the tumour’s size, location, and impact on surrounding structures.
Treatment options for meningiomas depend on the tumour’s size, location, growth rate, and the patient’s overall health. Observation, or “watchful waiting,” may be recommended for small, asymptomatic tumours. Surgical removal is often the preferred treatment for symptomatic or growing meningiomas. In some cases, radiation therapy may be used as a standalone treatment or following surgery to target any remaining tumour cells.
Early detection and treatment of meningiomas are crucial for preventing complications and improving outcomes. While many meningiomas grow slowly, they can eventually cause significant neurological problems as they increase in size. Timely medical intervention can alleviate symptoms, remove or reduce the size of the tumour, and minimize the risk of long-term damage.
Conclusion
This case exemplifies the high standard of neurosurgical care provided at International Modern Hospital. The successful management of this complex case, from precise diagnosis to effective surgical intervention and postoperative care, highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in treating neurological conditions. The utilization of advanced surgical techniques and the skillful coordination between surgical, nursing, and rehabilitation teams contributed significantly to the patient’s rapid recovery and return to everyday life.
Moreover, this case underscores the critical role of timely medical intervention in managing neurological conditions. Patients experiencing symptoms such as sudden onset weakness, numbness, or other neurological deficits should seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are paramount in achieving favourable outcomes in conditions like meningioma, where the progression of symptoms can lead to significant morbidity.
In conclusion, the successful treatment of this meningioma case at International Modern Hospital demonstrates the institution’s capability to handle complex neurosurgical cases with high precision and care. It serves as a testament to the hospital’s dedication to providing high-quality healthcare and emphasizes the importance of not delaying seeking medical help for neurological complaints. If you or someone you know is experiencing similar symptoms, do not hesitate to visit the hospital for evaluation and care.
