Keep your kidneys healthy by taking adequate amount of liquids. This means drinking the right amount of water for you. A common misconception is that everyone should drink eight glasses of water per day, but since everyone is different, daily water needs will vary by person. How much water you need is based on differences in age, climate, exercise intensity, as well as states of pregnancy, breastfeeding, and illness.
About 60-70% of your body weight is made up of water, and every part of your body needs it to function properly. Water helps the kidneys remove wastes from your blood in the form of urine. Water also helps keep your blood vessels open so that blood can travel freely to your kidneys, and deliver essential nutrients to them. But if you become dehydrated, then it is more difficult for this delivery system to work. Mild dehydration can make you feel tired, and can impair normal bodily functions. Severe dehydration can lead to kidney damage, so it is important to drink enough when you work or exercise very hard, and especially in warm and humid weather.
Here are 6 tips to make sure you’re drinking enough water and to keep your kidneys healthy:
-
Eight is great, but not for all.
 There is no rule that everyone needs at least 8 glasses of water a day. This is just a general recommendation, because we continually lose water from our bodies, and that we need adequate water intake to survive. It is estimated that men need approximately 13 cups (3 liters) of fluid daily, and that women need approximately 9 cups (2.2 liters) of fluid daily on an average.
There is no rule that everyone needs at least 8 glasses of water a day. This is just a general recommendation, because we continually lose water from our bodies, and that we need adequate water intake to survive. It is estimated that men need approximately 13 cups (3 liters) of fluid daily, and that women need approximately 9 cups (2.2 liters) of fluid daily on an average. -
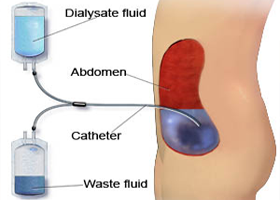
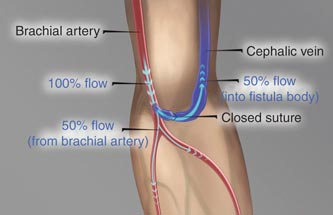
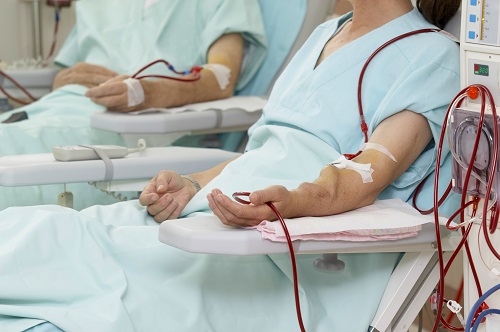
Less is wise, if you have kidney failure (end stage kidney disease). When the kidneys fail, people don’t excrete enough water, if any at all. For those who are receiving dialysis treatment, water must actually be strictly controlled.
-
It’s possible to drink lots of water.
 Athletes and sportsmen / sportswomen may drink large amounts of water and thereby dilute the sodium level in their blood, resulting in a dangerous condition called hyponatremia which may even cause rapid brain damage.
Athletes and sportsmen / sportswomen may drink large amounts of water and thereby dilute the sodium level in their blood, resulting in a dangerous condition called hyponatremia which may even cause rapid brain damage. -
Your urine says it all. Drinking enough water or other healthy fluids, such as unsweetened juice or low fat milk to quench thirst will keep your urine light yellow or colorless. When your urine is dark yellow, this indicates that you are dehydrated. In the ,idle east, especially in hot and humid conditions, one should be making at least 2 liters of urine daily.
-
H2O helps prevent kidney stones and UTIs. Kidney stones and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are two common medical conditions that can hurt the kidneys, and for which good hydration is very much essential. Kidney stones form less easily when there is sufficient water available to prevent stone-forming crystals from sticking together. Water helps dissolve the antibiotics used to treat urinary tract infections, making them more effective. Drinking enough water also helps produce more urine, which helps to flush out infection-causing bacteria.
-
Beware of medications.
 Drinking extra water with certain medications or before and after procedures with contrast dye may help prevent kidney damage. Read medication labels and ask questions before undergoing medical procedures involving contrast dyes. Always consult with your healthcare provider first though, especially if you are on a fluid restriction.
Drinking extra water with certain medications or before and after procedures with contrast dye may help prevent kidney damage. Read medication labels and ask questions before undergoing medical procedures involving contrast dyes. Always consult with your healthcare provider first though, especially if you are on a fluid restriction.


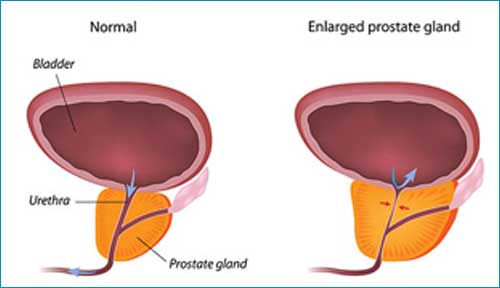
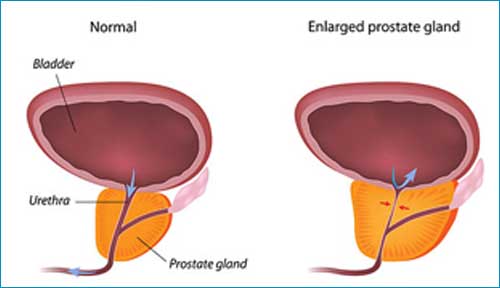 Surgical treatment of prostate enlargement is one of the most commonly performed operations in urology and is quite effective. Of course, as in any operation, there are side effects; but incidence of major side-effects in good hands are negligible. Moreover, this is an endoscopic operation without making any cuts in the body and has very short hospital stay, the added advantage being avoidance of side-effects due to medications.
Surgical treatment of prostate enlargement is one of the most commonly performed operations in urology and is quite effective. Of course, as in any operation, there are side effects; but incidence of major side-effects in good hands are negligible. Moreover, this is an endoscopic operation without making any cuts in the body and has very short hospital stay, the added advantage being avoidance of side-effects due to medications.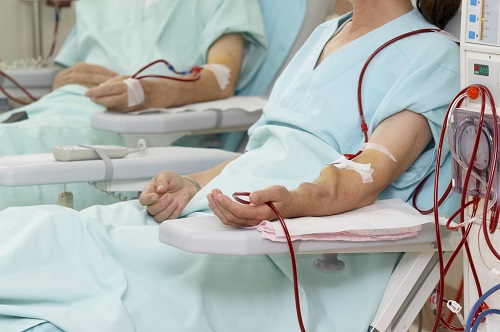
 hemoglobin and cardiac and nerve and brain damages.
hemoglobin and cardiac and nerve and brain damages.